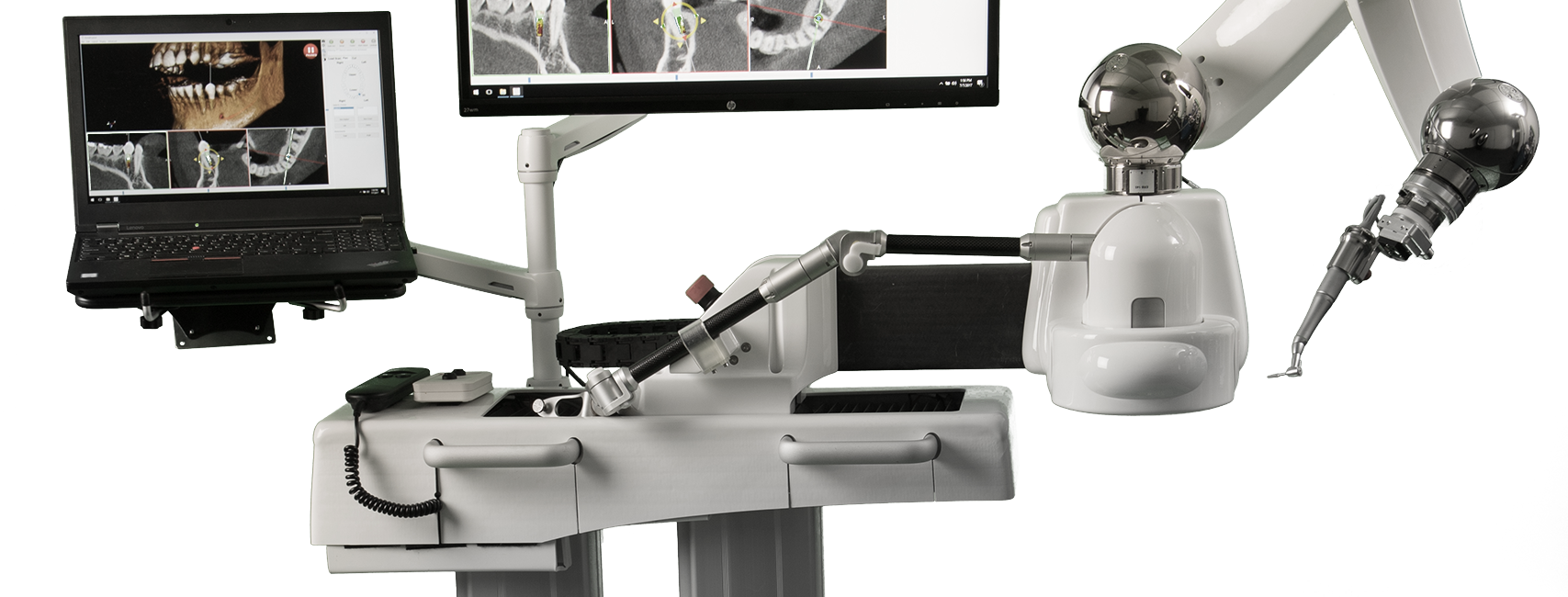
The field of dentistry has witnessed significant technological advancements over the years, with one of the most notable being the integration of robotics into dental practices. Robotic dentistry represents a revolutionary approach that combines the expertise of programmers and dentists to create innovative solutions for oral care. This collaborative effort not only enhances the precision and efficiency of dental procedures but also opens up new possibilities for the future of dentistry. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of robotic dentistry, the collaboration between programmers and dentists, and the potential benefits and challenges associated with this transformative approach.
The Evolution of Robotic Dentistry
The integration of robotics into dentistry marks a significant evolution in the field. Traditional dental procedures have relied on manual techniques and tools, often leading to variations in precision and outcomes. With the advent of robotics, dental procedures can now be executed with unparalleled accuracy and consistency.
Robotic systems, equipped with advanced sensors and imaging technologies, allow for precise measurements and real-time feedback during procedures. This level of precision is particularly crucial in delicate dental surgeries and interventions. The evolution of robotic dentistry reflects the continuous pursuit of improving patient outcomes and streamlining dental workflows.
The Collaborative Effort: Dentists and Programmers Unite
The success of robotic dentistry hinges on the collaboration between dentists and programmers. Dentists bring their extensive knowledge of oral anatomy, diagnostic skills, and treatment expertise, while programmers contribute their skills in robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and software development. This collaborative effort ensures that robotic systems are not only technologically advanced but also aligned with the practical requirements of dental practice.
Dentists and programmers work together to develop robotic systems that can perform a wide range of dental procedures, from routine cleanings to complex surgeries. The interdisciplinary nature of this collaboration fosters innovation and results in solutions that address the unique challenges of dentistry.
Key Components of Robotic Dentistry
a. Robotics and Automation:
Robotic arms and instruments designed for precise movements.
Automation of repetitive tasks, reducing human error and fatigue.
b. Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI algorithms for image analysis and interpretation.
Machine learning models for predictive diagnostics and treatment planning.
c. Sensors and Imaging Technologies:
Integration of advanced sensors for real-time feedback.
High-resolution imaging for accurate diagnostics and treatment visualization.
d. Haptic Feedback Systems:
Incorporation of haptic feedback to provide a sense of touch for the dentist, enhancing the operator’s control during procedures.
e. Tele-dentistry:
Remote operation of robotic systems, allowing expert dentists to perform procedures from a distance.
Increased accessibility to specialized dental care in underserved areas.
Benefits of Robotic Dentistry:
a. Precision and Consistency:
Robotic systems offer unmatched precision in dental procedures, minimizing the risk of errors.
Consistent outcomes across procedures, reducing variability in treatment results.
An example is programming digital smile design with absolute precision which elicits human smiles all around – from dentists and patients alike.
b. Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities:
AI-powered diagnostic tools improve the accuracy of disease detection.
Early identification of oral health issues, leading to proactive and preventive interventions.
c. Improved Ergonomics:
Robotic systems can access challenging areas with greater ease, enhancing the ergonomics of dental procedures.
Reduced physical strain on dentists, contributing to the overall well-being of dental professionals.
d. Time Efficiency:
Automation of certain tasks speeds up the overall treatment process.
Increased patient turnover without compromising the quality of care.
e. Remote Accessibility:Tele-dentistry facilitates access to dental care in remote or underserved areas.
Expert dentists can remotely assist or perform procedures, expanding the reach of specialized care.
Challenges and Considerations:
a. Cost and Accessibility:
Initial setup costs for robotic systems can be high, limiting accessibility for smaller practices.
Ongoing maintenance and software updates may contribute to additional expenses.
b. Integration with Traditional Practices:
Transitioning from traditional to robotic dentistry requires training and adaptation.
Ensuring a seamless integration with existing dental workflows is crucial for widespread adoption.
c. Ethical and Legal Considerations:
Clear guidelines and regulations are needed to address ethical concerns related to remote operation and AI decision-making.
Legal frameworks must be established to govern liability in cases of robotic system malfunctions.
d. Patient Acceptance:
Some patients may be apprehensive about receiving dental care from robotic systems.
Effective communication and education are essential to garner patient trust and acceptance.
The Future of Robotic Dentistry
Robotic dentistry is poised to play an increasingly prominent role in the future of oral care. It’s a space where scigentasy, scidentistry and dental fantasy converge happily. As technology continues to advance, new possibilities emerge for expanding the scope of robotic interventions. Some potential future developments include:
a. Customized Treatment Plans:
AI-driven algorithms could analyze individual patient data to create personalized treatment plans.
Tailored interventions based on a patient’s unique oral health profile.
b. Augmented Reality (AR) Integration:
AR systems could provide dentists with real-time, augmented visualizations during procedures.
Enhanced treatment precision through immersive, data-rich environments.
c. Advancements in Tele-dentistry:
Improved connectivity and communication technologies for more seamless remote operations.
Increased collaboration among dental professionals globally, sharing expertise and knowledge.
d. Expanded Scope of Robotic Procedures:
Robotic systems may evolve to perform a broader range of dental procedures, including more complex surgeries.
Integration with other medical specialties for comprehensive healthcare solutions.
e. Patient-Centric Innovations:
Focus on developing robotic systems that prioritize patient comfort and experience.
User-friendly interfaces and personalized care options.
Dentists Are Still Much Required: For Now
Robotic dentistry represents a transformative approach to oral care, combining the expertise of dentists and programmers to create innovative solutions. The collaborative effort has resulted in systems that offer unparalleled precision, consistency, and diagnostic capabilities. While challenges exist, the potential benefits, including improved patient outcomes and expanded accessibility to dental care, make robotic dentistry a promising frontier in the evolution of healthcare.
As technology continues to advance, the integration of robotics, AI, and automation into dental practices is likely to become more widespread. The ongoing collaboration between dentists and programmers will play a crucial role in shaping the future of robotic dentistry, ultimately redefining the standards of oral care and paving the way for a new era in dentistry.