Dental implants have revolutionized the field of dentistry, offering a permanent solution to tooth loss while improving oral health and overall quality of life. With their ability to mimic the appearance and function of natural teeth, dental implants have become a popular choice for patients seeking a long-lasting alternative to dentures or bridges. However, not all implants are created equal. From types to materials, understanding your options can help you make an informed decision tailored to your needs.
What Are Dental Implants?
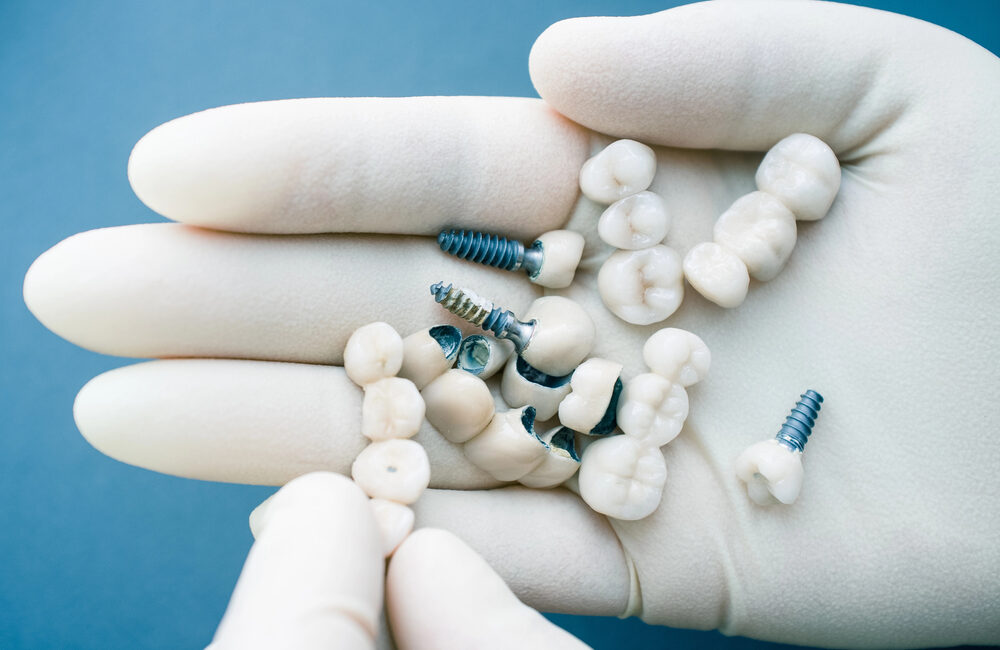
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots made from biocompatible materials, primarily designed to support replacement teeth such as crowns, bridges, or dentures. They are surgically placed into the jawbone, where they fuse with the bone through a process called osseointegration. This fusion provides a sturdy foundation, ensuring durability and functionality comparable to natural teeth.
Types of Dental Implants
There are three primary types of dental implants:
1. Endosteal Implants
These are the most common types of dental implants. Shaped like small screws or cylinders, endosteal implants are placed directly into the jawbone. Once the surrounding bone heals, a second surgery is performed to attach an abutment, which holds the replacement tooth in place. This option is ideal for patients with healthy jawbones that can support the implant.
2. Subperiosteal Implants
Unlike endosteal implants, subperiosteal implants are placed beneath the gum tissue but on top of the jawbone. This type is typically recommended for patients who lack sufficient bone height or density and cannot undergo bone augmentation procedures. Subperiosteal implants consist of a metal framework that supports one or more replacement teeth.
3. Zygomatic Implants
Zygomatic implants are less common and are used in cases where there is severe bone loss in the upper jaw. Instead of being anchored in the jawbone, these implants are placed in the zygomatic bone, or cheekbone. Due to their complexity, they require specialized expertise.
Materials Used in Dental Implants
The choice of material for dental implants is crucial for their success and longevity. The two most commonly used materials are:
1. Titanium
Titanium has been the gold standard for dental implants for decades. It is biocompatible, lightweight, and durable, making it an excellent choice for osseointegration. Titanium implants are also versatile, available in two-piece systems that allow for customizable abutments. However, in rare cases, patients with metal sensitivities may experience allergic reactions.
2. Zirconia
Zirconia implants are a metal-free alternative gaining popularity for their aesthetic advantages. Their tooth-colored appearance makes them ideal for patients concerned about visible metal components. Zirconia is also biocompatible and resistant to corrosion. However, zirconia implants are typically designed as a one-piece system, which can limit flexibility in certain cases.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Dental Implants
Selecting the right type and material for your dental implants involves several considerations:
– Bone Health: Patients with insufficient jawbone density may require bone grafting or alternative solutions like subperiosteal or zygomatic implants.
– Aesthetic Preferences: Zirconia implants are more visually appealing, especially for front teeth.
– Budget: Titanium implants are generally more affordable and widely available compared to zirconia.
– Medical History: Discuss any allergies or sensitivities with your dentist to ensure a suitable material is chosen.
– Lifestyle: Smokers or patients with chronic conditions like diabetes may require special precautions to ensure successful outcomes.
Dental Implants and Long-Term Care
Proper maintenance is essential to prolong the lifespan of dental implants. Just like natural teeth, implants require regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups. Using a suitable mouthwash can help reduce plaque buildup and maintain gum health. However, it’s important to choose a mouthwash carefully.
Recent studies have raised concerns about the prolonged use of certain mouthwashes and their association with the development of oral cancers. Some mouthwashes contain high levels of alcohol or other chemicals that may irritate the oral mucosa, potentially increasing cancer risks over time. While the evidence is not conclusive, it’s advisable to opt for alcohol-free mouthwash and consult your dentist for personalized recommendations.
Benefits of Dental Implants
Dental implants offer numerous advantages over traditional tooth replacement methods:
1. Improved Aesthetics: Implants look and feel like natural teeth, enhancing your smile and confidence.
2. Durability: With proper care, dental implants can last a lifetime.
3. Bone Preservation: Implants stimulate the jawbone, preventing bone loss that often occurs with missing teeth.
4. Functionality: They restore full chewing and speaking capabilities, unlike removable dentures.
5. Convenience: Unlike dentures, implants eliminate the need for adhesives and daily removal.
The Future of Dental Implants
Advancements in dental technologies continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible with implants. Innovations such as 3D printing, guided surgery, and nanotechnology are enhancing precision, reducing recovery times, and improving success rates. Additionally, researchers are exploring bioactive coatings that can further promote bone integration and reduce the risk of infections.
Dental implants are a remarkable solution for replacing missing teeth, offering both functional and aesthetic benefits. Whether you’re considering titanium or zirconia implants, understanding the types, materials, and associated risks is crucial for making an informed decision. Additionally, while caring for your oral health, be mindful of the products you use, such as mouthwash, to minimize potential risks like the development of oral cancers.
Consulting with a qualified dental professional will help you navigate your options and achieve the best possible outcome for your smile and oral health.