When it comes to oral health, it doesn’t only boil down to the brightness or straightness of your teeth. It also includes your gums. You are not immune to various gum diseases just because you lack cavities. Because gum diseases tend to be painless, most people don’t realise that something is wrong with their gums.
The term gingiva is the anatomical term referring to gums which surround your teeth inside the mouth. The gingiva consists of mucosal tissue covering the mandible and maxilla and finishing at each tooth’s neck. The gingiva is divided into marginal gingiva, gingival sulcus, and attached gingiva.
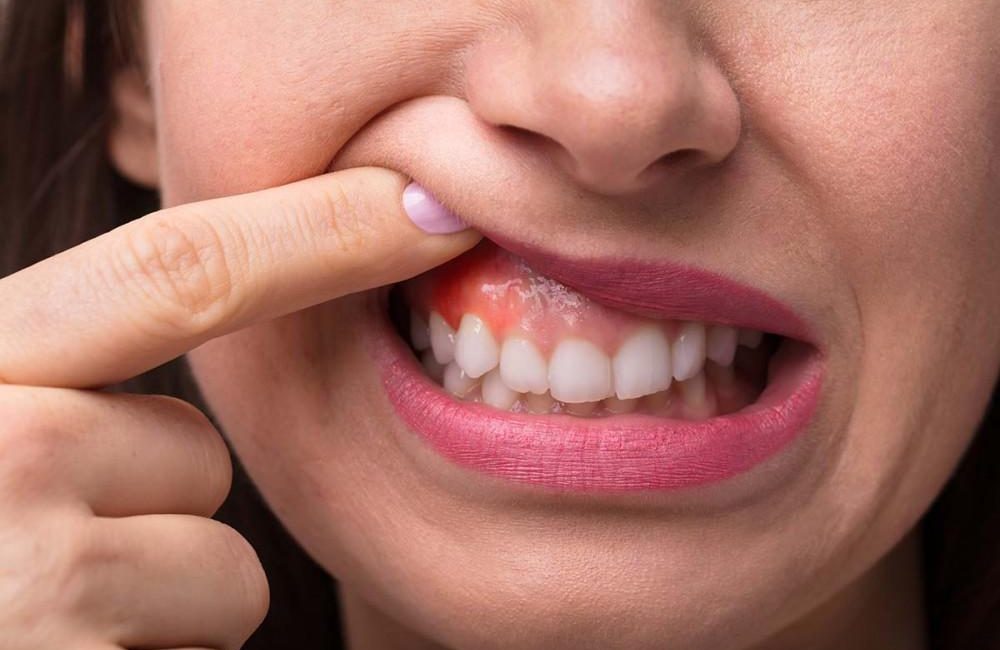
Gingivitis is the first stage of gum disease, and once it has progressed, it could result in tooth loss. Fortunately, it is preventable, and there are effective periodontal treatments for gingivitis gum diseases.
Causes of gingivitis
The primary cause of this gum disease is poor oral hygiene which encourages plaque to form on your teeth, subsequently inflaming the surrounding gum tissue. Here are other reasons;
- Chewing or smoking tobacco
- Dry mouth
- Poor nutrition, such as a vitamin C deficiency
- A dry mouth
- Older age
- Health conditions that lower body immunity, e.g. leukaemia, cancer treatment or HIV/AIDS
- Poorly fitting dental restorations or crooked teeth that are tough to clean
- particular drugs such as some drugs used for epileptic seizures, high blood pressure and angina
- Genetics
- Hormonal changes, e.g. those related to birth control pill use, pregnancy or menstrual cycle
- Certain fungal and viral infections
Symptoms include swollen, red and inflamed gums that might bleed whenever you brush your teeth.
Easy tips to prevent gingivitis
- Brushing your teeth twice every day
Good oral hygiene is one of the best ways to prevent gingivitis. You should brush twice daily for two minutes during each session. Be sure to spend 30 seconds on either quarter of your mouth to prevent plaque from building up and the ensuing issues. It is crucial to remove plaque daily as it forms quickly, starting from when you stop brushing.
If plaque is left on for too long, it builds up into tartar, creating an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive and irritate your gums, hence gingivitis. The tartar should be removed by your dentist.
- Floss daily
Flossing involves cleaning your teeth below and along the gum line, which is vital for encouraging good oral hygiene and preventing gingivitis. When you floss every day, your gums remain healthy, and the floss removes any plaque that your toothbrush cannot remove.
Flossing also keeps food particles out of the sulcus, the space between the tooth and gum, protecting your gum fibres. Ultimately, it will help stop your gums from getting inflamed, tender, and bleeding. You can also use an antibacterial mouthwash.
- Stop chewing or smoking tobacco
Tobacco users are more predisposed to gingivitis than non-smokers. First, tobacco usage constricts facial blood, which lingers moments after use. Constriction causes inflammation. Another reason is that tobacco users have higher numbers of ‘harmful’ bacteria causing oral issues such as gingivitis.
Lastly, nicotine compromises cell protection in the gums. Therefore, tobacco users have a limited immune system that cannot clean up gingivitis-causing bacteria adequately.
Take away
Gingivitis is a pretty common oral disease, although it is preventable. There are several other oral health conditions you can learn about them using search engine optimisation to find out about medical issues. These tips provided above should help you get started too. If you suspect that you have it, consider visiting a dentist as soon as possible.